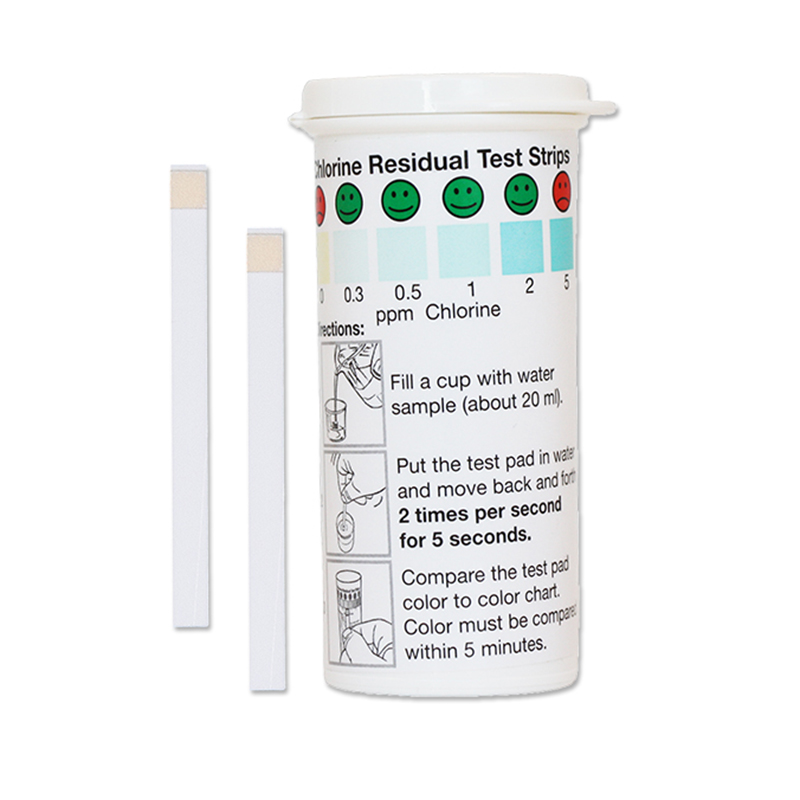
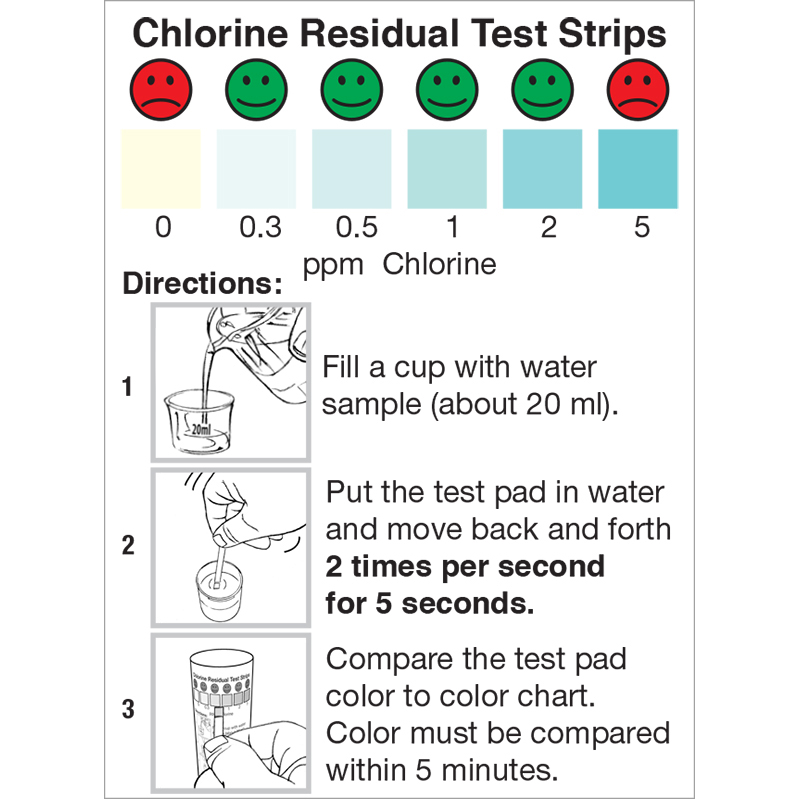
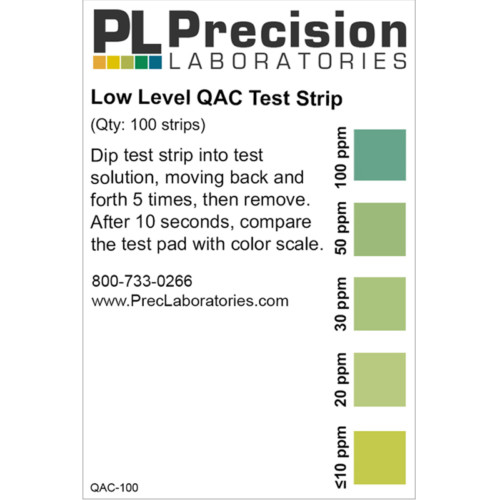
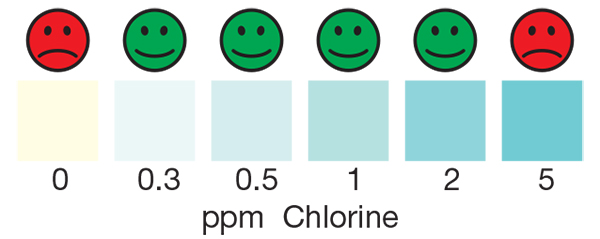
The Residual Chlorine test strip is for use in ensuring free chlorine levels in drinking water are sufficient to inactivate the bacteria and viruses that cause diarrheal disease, as well as ensuring the water is protected from re-contamination during storage. The strip can also be used to ensure systems have no residual free chlorine after chemical sanitization by testing for very low levels of free chlorine in solution from 0.0 ppm – 5.0 ppm. The residual chlorine test strip is accurate within 5-10% of reading the color scale. The vial is sold with an illustrative color chart, which is helpful when testing drinking water from chlorine kits in developing countries.
Residual Chlorine Test Strip, 5ppm
Residual Chlorine Test Strip, 5ppm
- Fill a cup with water sample (about 20mL) or dip the test strip directly into the solution.
- With the test pad in the water, move back and forth 2 times per second for 5 seconds.
- Remove the test strip, and compare to the color chart within 5 minutes.
CHLVL05; CHL-05; CHL-05-1V-50
Product Specs
| SKU: | CHL-05-1V-50 |
|---|---|
| Strip Quantity: | 50 strips |
| Vial Dimensions: | 1.125″ (D) x 3.375″ (H) [29mm (D) x 86mm (H)] |
| Strip Dimensions: | 2.5" (L) x .1875" (W) [64mm (L) x 5mm (W)] |
| Weight: | 0.07 lbs [33.4 g] (50-strip vial) |
| Other: | Stored in a flip-top vial with built-in desiccant liner. |
| Shelf-Life: | 2 Years |
| Label: | Pre-printed Precision label |
Product Documentation
SDS
Fact Sheet
Videos
Do the Chlorine test strips only detect chlorine or do they also change color in salt concentrations (NaCl)?
Sodium chloride salt is not an oxidizer and will not react with any of our chlorine strips.
However, if you are using salt in pools as a source of chlorine, and your question is, “Can I use chlorine test strips in a salt water pool?”, the answer is yes. In this instance, you must use a chlorine test strip with the correct range, such as the Residual Chlorine 0-5ppm or Low Level Chlorine 0-10ppm test strips.
Salt is used to introduce chlorine to the water (no reaction to strips) but the salt generator or electrolysis unit takes the salt water and converts it to hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite. It is the hypochlorius acid and hypochlorite ions that are commonly referred to as “available chlorine.” Hypochlorous acid is a strong oxidizer and will react with any of the chlorine strips.
What is the ideal pH of an available chlorine solution?
All available chlorine has some biocide strength, although hypochlorous acid is a far stronger biocide than hypochlorite ion or the chloramines. In solutions at pH of 5-7, hypochlorous acid is the most prevalent species. For this reason, most sanitizing solutions will work best in the neutral to slightly acidic pH range.
What is the difference between free available, combined available, and total available chlorine?
When chlorine gas (Cl2) or bleach (sodium hypochlorite or NaOCl) is added to water the result is the formation of hypochlorous acid (HClO).
Cl2 + H2O -> HOCl + H+ + Cl-
NaOCl +H2O -> HOCl + Na+ + OH-
Depending on the pH of the solution the hypochlorous acid exists in solution as either hypochlorous acid (HClO) or hypochlorite ion (OCl-).
HOCl OCl- + H+
Free available chlorine refers to the amount of hypochlorous acid AND hypochlorite ions present.
Combined (or bound) available chlorine arises when nitrogen (usually in the form of ammonia) is present to form what are called chloramines (mono-, di-, and trichloramines are possible).
Total available chlorine is the sum of the free available chlorine and the combined available chlorine.